Economic Survey & Budget 2024
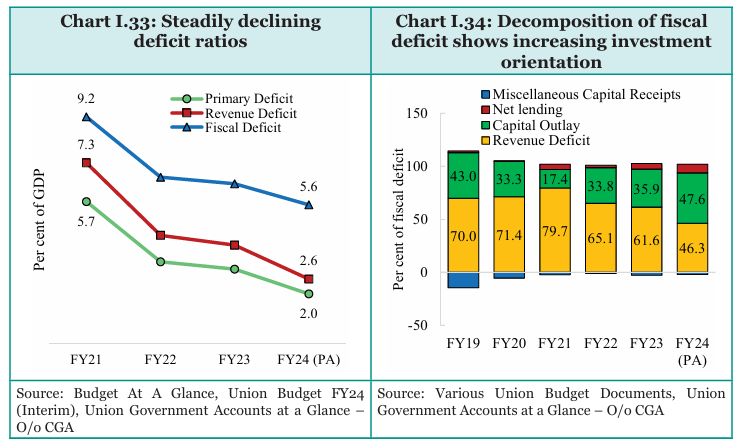
Fiscal Consolidation and Fiscal Prudence
Why is India having Jobless Growth Scenario?
Direct Tax Reforms
Arvind Modi Panel
Akhilesh Ranjan Panel
Challenges of Manufacturing Sectors, esp. MSME
Infrastructure Deficit in India
Energy Security
Agrarian Economy Issues
Urban/Rural Economy
Startup Economy (Angel Tax Removed)
Labour Sectors Reforms
Social Sector Development
State of the Indian Economy
High Economic Growth and Low Inflation
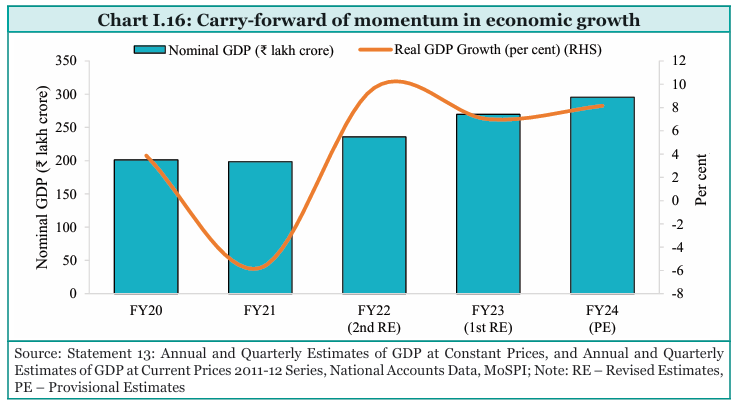
India is having a long-term economic stability due to the monetary stability created by RBI. India's economy carried forward the momentum it built in FY23 into FY24 despite a gamut of global and external challenges.
The focus on maintaining macroeconomic stability ensured that these challenges had minimal impact on India’s economy. As a result, India’s real GDP grew by 8.2 percent in FY24, posting growth of over 7 percent for a third consecutive year, driven by stable consumption demand and steadily improving investment demand.
On the supply side, gross value-added (GVA) in 2011–12 prices grew by 7.2 percent in FY24, with growth remaining broad-based.
Net taxes at constant (2011–12) prices grew by 19.1 percent in FY24, aided by reasonably strong tax growth, both at the center and state levels and rationalization of subsidy expenditure. This led to the difference between GDP and GVA growth in FY24.
Real GDP growth FY23 | 8.2% |
|---|---|
CPI | 4–6% |
Macroeconomic Vulnerabilities, the three problems of Indian Economy
Inflation
Current Account Deficit
Low GDP growth
Fiscal Consolidation Approach